Cobol is a major language on VMS.
Cobol is not a major language on *nix and Windows, but it is used some places.
There are several Cobol offerings available for *nix and Windows - most widely used and most well-known is probably MicroFocus.
But there is also an open source option - GnuCOBOL.
Obviously it can be relevant to move files between the two environments:
Plain sequential files can just be transferred as text between the systems and should work.
Indexed files can not just be transferred and work.
VMS Cobol use RMS index-sequential files for indexed files and GnuCOBOL use either BDB or VBISAM for indexed files. And those file formats are not compaitble. So a conversion is required.
This article shows how to convert between VMS Cobol indexed files and either GnuCOBOL with BDB indexed files or GnuCOBOL with VBISAM indexed files.
IMPORTANT: check BDB licenses (AGPL and Oracle commercial license) before using BDB.
There are two ways to do these conversions:
Two step:
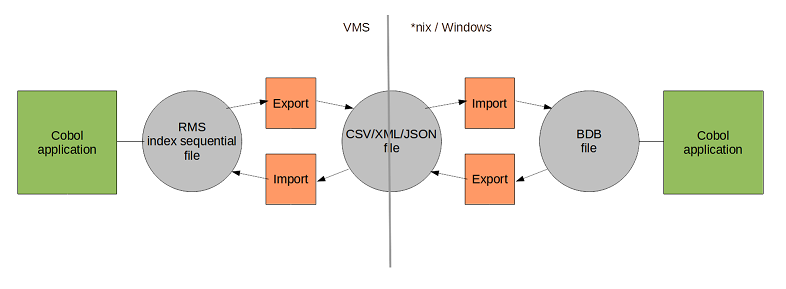
This solution is relative simple/trivial but can require a significant effort to code the custom export and import code.
One step:
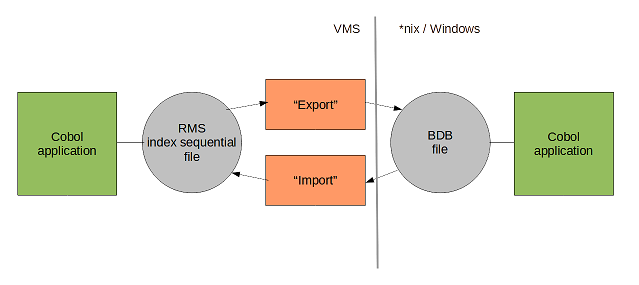
This solution is more tricky but will typical require a lot less code.
And this is the approach that will be used in this article.
Note that I am not a Cobol programmer so the Cobol code may not be "real Cobol style", but it seems to work.
Background info:
To use this you will need:
If you want to use Cobol for the conversion you will additionally need:
If you want to use Jython (JVM Python) for the conversion instead of Cobol you will additionally need:
The conversion will assume GnuCOBOL on *nix or Windows is configured to use little endian integers. This is not the default but is native for x86-64. If big endian then an additional byte swap is required on all integers.
All the Cobol programs will use this D.COB for Cobol indexed file definition:
FD D-FILE.
01 D-RECORD.
03 D-ID PIC X(8).
03 D-IV PIC 9(8) COMP.
03 D-ZV PIC 9(5)V9(2) PACKED-DECIMAL.
03 D-SLEN PIC 9(4) COMP.
03 D-SV PIC X(50).
Code (portable):
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. CREA.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NREC PIC 9(4) COMP VALUE 10.
01 I PIC 9(4) DISPLAY.
01 WID PIC 9(4) DISPLAY.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
PERFORM VARYING I FROM 1 BY 1 UNTIL I > NREC
COMPUTE WID = 1000 + I
STRING "Key#" DELIMITED BY SIZE WID DELIMITED BY SIZE INTO D-ID
COMPUTE D-IV = I
COMPUTE D-ZV = I + 0.50
COMPUTE D-SLEN = 18
STRING "This is value " DELIMITED BY SIZE I DELIMITED BY SIZE INTO D-SV
WRITE D-RECORD
INVALID KEY DISPLAY "Error writing"
NOT INVALID KEY CONTINUE
END-WRITE
END-PERFORM
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
Build and run on VMS:
$ cobol crea
$ link crea
$ run crea
Build and run on Windows:
cobc -Wall -free -conf=le.conf -x crea.cob
crea
(for VBISAM on VMS drop the .ISQ extension as VBISAM creates .DAT and .IDX files)
First export.
You generate the file on VMS, convert it to BDB format and transfer it binary to *nix or Windows.
Code:
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. EXP.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 BDB PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 D2-RECORD.
03 D2-ID PIC X(8).
03 D2-IV PIC 9(8) COMP.
03 D2-ZV PIC 9(5)V9(2) PACKED-DECIMAL.
03 D2-SLEN PIC 9(4) COMP.
03 D2-SV PIC X(50).
01 EOF-FLAG PIC X.
01 STAT PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 STAT2 PIC 9(9) DISPLAY.
01 D2-LEN PIC S9(9) COMP VALUE 68.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
CALL "db_open"
USING
BY DESCRIPTOR "TEST.BDB"
GIVING
BDB
END-CALL
MOVE 'N' TO EOF-FLAG
PERFORM UNTIL EOF-FLAG = 'Y'
READ D-FILE NEXT
AT END MOVE 'Y' TO EOF-FLAG
NOT AT END PERFORM CONV-PARAGRAPH
END-READ
END-PERFORM
CALL "db_close"
USING
BY REFERENCE BDB
END-CALL
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
CONV-PARAGRAPH.
MOVE D-ID TO D2-ID
MOVE D-IV TO D2-IV
MOVE D-ZV TO D2-ZV
MOVE D-SLEN TO D2-SLEN
MOVE D-SV TO D2-SV
CALL "db_sk_put"
USING
BY REFERENCE BDB
BY DESCRIPTOR D2-ID
BY REFERENCE D2-RECORD
BY REFERENCE D2-LEN
GIVING
STAT
END-CALL
IF STAT = 0 THEN
DISPLAY D2-ID " CONVERTED"
ELSE
MOVE STAT TO STAT2
DISPLAY D2-ID " FAILED WITH STATUS " STAT2
END-IF.
Build and run:
$ cobol/name=as_is exp
$ link exp + pbdbdir:pbdb/opt + pbdbdir:bdb/opt
$ run exp
Next import.
You generate the file on *nix or Windows, transfer it binary to VMS and convert it from BDB format.
Code:
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. IMP.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 BDB PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 CUR PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 D2-RECORD.
03 D2-ID PIC X(8).
03 D2-IV PIC 9(8) COMP.
03 D2-ZV PIC 9(5)V9(2) PACKED-DECIMAL.
03 D2-SLEN PIC 9(4) COMP.
03 D2-SV PIC X(50).
01 STAT PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 STAT2 PIC 9(9) DISPLAY.
01 D2-LEN PIC S9(9) COMP VALUE 68.
01 ID PIC X(8).
01 DUMMY PIC S9(9) COMP.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
CALL "db_open"
USING
BY DESCRIPTOR "TEST.BDB"
GIVING
BDB
END-CALL
CALL "db_cursor_open"
USING
BY REFERENCE BDB
GIVING
CUR
END-CALL
MOVE 0 TO STAT
PERFORM UNTIL STAT NOT = 0
CALL "db_cursor_sk_next"
USING
BY REFERENCE CUR
BY DESCRIPTOR ID
BY REFERENCE DUMMY
BY REFERENCE D2-RECORD
BY REFERENCE D2-LEN
BY REFERENCE DUMMY
GIVING
STAT
END-CALL
IF STAT = 0
PERFORM CONV-PARAGRAPH
END-IF
END-PERFORM
CALL "db_close"
USING
BY REFERENCE BDB
END-CALL
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
CONV-PARAGRAPH.
MOVE D2-ID TO D-ID
MOVE D2-IV TO D-IV
MOVE D2-ZV TO D-ZV
MOVE D2-SLEN TO D-SLEN
MOVE D2-SV TO D-SV
WRITE D-RECORD
INVALID KEY DISPLAY D-ID " FAILED"
NOT INVALID KEY DISPLAY D-ID " CONVERTED"
END-WRITE.
Build and run:
$ cobol/name=as_is imp
$ link imp + pbdbdir:pbdb/opt + pbdbdir:bdb/opt
$ run imp
If you are in a Cobol world then using Cobol to convert the data files are a pretty obvious choice.
But in case that data conversions fall under a different team than applications or if it is decided to do som changes to data now it is being touched anyway, then being able to write the conversion code in Python may be convenient.
Data class for VMS index-sequential files:
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import dk.vajhoej.isam.KeyField;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Alignment;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Endian;
import dk.vajhoej.record.FieldType;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Struct;
import dk.vajhoej.record.StructField;
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data implements Serializable {
@KeyField(n=0)
@StructField(n=0, type=FieldType.FIXSTRNULTERM, length=8)
private String id;
@StructField(n=1, type=FieldType.INT4)
private int iv;
@StructField(n=2, type=FieldType.PACKEDBCD, length=4, decimals=2)
private BigDecimal zv;
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public Data() {
this("", 0, BigDecimal.ZERO, "");
}
public Data(String id, int iv, BigDecimal zv, String sv) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.iv = iv;
this.zv = zv;
this.sv = sv;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getIv() {
return iv;
}
public void setIv(int iv) {
this.iv = iv;
}
public BigDecimal getZv() {
return zv;
}
public void setZv(BigDecimal zv) {
this.zv = zv;
}
public String getSv() {
return sv;
}
public void setSv(String sv) {
this.sv = sv;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{iv: %d, zv: %s, sv: %s}", iv, zv, sv);
}
}
Data class for BDB files:
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Alignment;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Endian;
import dk.vajhoej.record.FieldType;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Struct;
import dk.vajhoej.record.StructField;
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
@StructField(n=0, type=FieldType.FIXSTRNULTERM, length=8)
private String id;
@StructField(n=1, type=FieldType.INT4)
private int iv;
@StructField(n=2, type=FieldType.PACKEDBCD, length=4, decimals=2)
private BigDecimal zv;
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public Data2() {
this("", 0, BigDecimal.ZERO, "");
}
public Data2(String id, int iv, BigDecimal zv, String sv) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.iv = iv;
this.zv = zv;
this.sv = sv;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getIv() {
return iv;
}
public void setIv(int iv) {
this.iv = iv;
}
public BigDecimal getZv() {
return zv;
}
public void setZv(BigDecimal zv) {
this.zv = zv;
}
public String getSv() {
return sv;
}
public void setSv(String sv) {
this.sv = sv;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{iv: %d, zv: %s, sv: %s}", iv, zv, sv);
}
}
Utility class:
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class AutoMap<TFROM,TTO> {
public static class MethodPair {
private Method getter;
private Method setter;
private boolean trim;
public MethodPair(Method getter, Method setter, boolean trim) {
this.getter = getter;
this.setter = setter;
this.trim = trim;
}
public Method getGetter() {
return getter;
}
public Method getSetter() {
return setter;
}
public boolean getTrim() {
return trim;
}
}
private List<MethodPair> conv;
public AutoMap(Class<TFROM> from, Class<TTO> to) throws IntrospectionException {
this(from, to, false);
}
public AutoMap(Class<TFROM> from, Class<TTO> to, boolean trim) throws IntrospectionException {
conv = new ArrayList<MethodPair>();
for(PropertyDescriptor pdfrom : Introspector.getBeanInfo(from).getPropertyDescriptors()) {
for(PropertyDescriptor pdto : Introspector.getBeanInfo(to).getPropertyDescriptors()) {
if(pdfrom.getName().equals(pdto.getName())) {
Method getter = pdfrom.getReadMethod();
Method setter = pdto.getWriteMethod();
if(getter != null && setter != null) {
conv.add(new MethodPair(getter, setter, trim && pdfrom.getPropertyType().equals(String.class)));
}
}
}
}
}
public void convert(TFROM from, TTO to) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
for(MethodPair mp : conv) {
if(mp.getTrim()) {
mp.getSetter().invoke(to, ((String)mp.getGetter().invoke(from)).trim());
} else {
mp.getSetter().invoke(to, mp.getGetter().invoke(from));
}
}
}
}
This code may appear excessive compared to the simple D.COB above and the two Data classes are practically identical, but the code does provide a lot of extra flexibility.
Changing:
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
to:
@Struct(endianess=Endian.BIG, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
will change integers in the BDB file from little endian to big endian (GnuCOBOL default!).
Changing:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
to:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50, encoding="ISO-8859-1")
private String sv;
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50, encoding="utf-8")
private String sv;
will convert the sv field from ISO-8859-1 to UTF-8. Remember if you do that then the field may grow in length!
And:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=4, type=FieldType.VAXFP4)
private float xv1;
@StructField(n=5, type=FieldType.VAXFP8)
private double xv2;
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=4, type=FieldType.FP4)
private float xv1;
@StructField(n=5, type=FieldType.FP8)
private double xv2;
will convert xv1 and xv2 from VAX F-float and VAX G-float to standard IEEE 32 bit float (S-float in VMS terminology) and standard IEEE 64 bit float (T-float in VMS terminology).
And AutoMap is just a utility class that does not change for different data classes.
Export.
Code:
from com.sleepycat.db import Database, DatabaseConfig, DatabaseType, DatabaseEntry
from dk.vajhoej.isam import Key0
from dk.vajhoej.isam.local import LocalIsamSource
from dk.vajhoej.record import StructWriter
import Data
import Data2
import AutoMap
def prep(s):
return DatabaseEntry(s.encode('utf-8'))
def serialize(d):
sw = StructWriter()
sw.write(d)
return DatabaseEntry(sw.bytes)
m = AutoMap(Data, Data2)
isq = LocalIsamSource('test.isq', 'dk.vajhoej.vms.rms.IndexSequential', False)
bdbcfg = DatabaseConfig()
bdbcfg.allowCreate = True
bdbcfg.type = DatabaseType.BTREE
bdb = Database('test.bdb', None, bdbcfg)
it = isq.readGE(Data, Key0(' '))
while it.read():
d = it.current()
d2 = Data2()
m.convert(d, d2)
bdb.put(None, prep(d2.id), serialize(d2))
print(d.id + ' converted')
bdb.close()
isq.close()
Run:
$ javac -classpath /dbdir/db.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/record.jar Data.java Data2.java AutoMap.java
$ define/nolog jython_libs "/dbdir/db.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/isam-vms.jar:/isamdir/record.jar ""-Dsleepycat.db.libname=db_java_wrap_shr"""
$ define/nolog db_java_wrap_shr disk2:[arne.bdb]db_java_wrap_shr.exe
$ jython exp.py
Import:
from com.sleepycat.db import Database, DatabaseConfig, DatabaseEntry, OperationStatus
from dk.vajhoej.isam import Key0
from dk.vajhoej.isam.local import LocalIsamSource
from dk.vajhoej.record import StructReader
import Data
import Data2
import AutoMap
def deserialize(o):
sr = StructReader(o)
return sr.read(Data2)
m = AutoMap(Data2, Data)
isq = LocalIsamSource('test.isq', 'dk.vajhoej.vms.rms.IndexSequential', False)
bdb = Database('test.bdb', None, DatabaseConfig())
it = bdb.openCursor(None, None)
k = DatabaseEntry()
v = DatabaseEntry()
stat = it.getFirst(k, v, None)
while stat == OperationStatus.SUCCESS:
d2 = deserialize(v.data)
d = Data()
m.convert(d2, d)
isq.create(d)
print(d2.id + ' converted')
stat = it.getNext(k, v, None)
bdb.close()
isq.close()
Run:
$ javac -classpath /dbdir/db.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/record.jar Data.java Data2.java AutoMap.java
$ define/nolog jython_libs "/dbdir/db.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/isam-vms.jar:/isamdir/record.jar ""-Dsleepycat.db.libname=db_java_wrap_shr"""
$ define/nolog db_java_wrap_shr disk2:[arne.bdb]db_java_wrap_shr.exe
$ create/fdl=sys$input test.isq
FILE
ORGANIZATION indexed
RECORD
FORMAT fixed
SIZE 68
KEY 0
SEG0_LENGTH 8
SEG0_POSITION 0
TYPE string
$
$ jython imp.py
(the CREATE/FDL is necessary because the ISAM library cannot create an index-sequential file only use an existing one)
First export.
You generate the file on VMS, convert it to VBISAM format and transfer them binary to *nix or Windows.
Code:
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. EXP.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 VBI PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 D2-RECORD.
03 D2-ID PIC X(8).
03 D2-IV PIC 9(8) COMP.
03 D2-ZV PIC 9(5)V9(2) PACKED-DECIMAL.
03 D2-SLEN PIC 9(4) COMP.
03 D2-SV PIC X(50).
01 EOF-FLAG PIC X.
01 STAT PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 STAT2 PIC 9(9) DISPLAY.
01 D2-LEN PIC S9(9) COMP VALUE 68.
01 RECLEN PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 KEYSTART PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 KEYLEN PIC S9(9) COMP.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
MOVE 68 TO RECLEN
MOVE 0 TO KEYSTART
MOVE 8 TO KEYLEN
CALL "db_create"
USING
BY DESCRIPTOR "TEST"
BY REFERENCE RECLEN
BY REFERENCE KEYSTART
BY REFERENCE KEYLEN
GIVING
VBI
END-CALL
MOVE 'N' TO EOF-FLAG
PERFORM UNTIL EOF-FLAG = 'Y'
READ D-FILE NEXT
AT END MOVE 'Y' TO EOF-FLAG
NOT AT END PERFORM CONV-PARAGRAPH
END-READ
END-PERFORM
CALL "db_close"
USING
BY REFERENCE VBI
END-CALL
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
CONV-PARAGRAPH.
MOVE D-ID TO D2-ID
MOVE D-IV TO D2-IV
MOVE D-ZV TO D2-ZV
MOVE D-SLEN TO D2-SLEN
MOVE D-SV TO D2-SV
CALL "db_put"
USING
BY REFERENCE VBI
BY REFERENCE D2-RECORD
GIVING
STAT
END-CALL
IF STAT = 0 THEN
DISPLAY D2-ID " CONVERTED"
ELSE
MOVE STAT TO STAT2
DISPLAY D2-ID " FAILED WITH STATUS " STAT2
END-IF.
Build and run:
$ cobol exp
$ link exp + vbidir:vms_vbisam + sys$input/opt
libvbisam/share
$
$ run exp
Next import.
You generate the files on *nix or Windows, transfer them binary to VMS and convert them from VBISAM format.
Code:
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. IMP.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 VBI PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 CUR PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 D2-RECORD.
03 D2-ID PIC X(8).
03 D2-IV PIC 9(8) COMP.
03 D2-ZV PIC 9(5)V9(2) PACKED-DECIMAL.
03 D2-SLEN PIC 9(4) COMP.
03 D2-SV PIC X(50).
01 STAT PIC S9(9) COMP.
01 STAT2 PIC 9(9) DISPLAY.
01 D2-LEN PIC S9(9) COMP VALUE 68.
01 ID PIC X(8).
01 DUMMY PIC S9(9) COMP.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
CALL "db_open"
USING
BY DESCRIPTOR "TEST"
GIVING
VBI
END-CALL
CALL "db_cursor_open"
USING
BY REFERENCE VBI
GIVING
CUR
END-CALL
MOVE 0 TO STAT
PERFORM UNTIL STAT NOT = 0
CALL "db_cursor_next"
USING
BY REFERENCE CUR
BY REFERENCE D2-RECORD
BY REFERENCE D2-LEN
GIVING
STAT
END-CALL
IF STAT = 0
PERFORM CONV-PARAGRAPH
END-IF
END-PERFORM
CALL "db_close"
USING
BY REFERENCE VBI
END-CALL
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
CONV-PARAGRAPH.
MOVE D2-ID TO D-ID
MOVE D2-IV TO D-IV
MOVE D2-ZV TO D-ZV
MOVE D2-SLEN TO D-SLEN
MOVE D2-SV TO D-SV
WRITE D-RECORD
INVALID KEY DISPLAY D-ID " FAILED"
NOT INVALID KEY DISPLAY D-ID " CONVERTED"
END-WRITE.
Build and run:
$ cobol imp
$ link imp + vbidir:vms_vbisam + sys$input/opt
libvbisam/share
$
$ run imp
If you are in a Cobol world then using Cobol to convert the data files are a pretty obvious choice.
But in case that data conversions fall under a different team than applications or if it is decided to do som changes to data now it is being touched anyway, then being able to write the conversion code in Python may be convenient.
Data class for VMS:
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import dk.vajhoej.isam.KeyField;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Alignment;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Endian;
import dk.vajhoej.record.FieldType;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Struct;
import dk.vajhoej.record.StructField;
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data implements Serializable {
@KeyField(n=0)
@StructField(n=0, type=FieldType.FIXSTRNULTERM, length=8)
private String id;
@StructField(n=1, type=FieldType.INT4)
private int iv;
@StructField(n=2, type=FieldType.PACKEDBCD, length=4, decimals=2)
private BigDecimal zv;
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public Data() {
this("", 0, BigDecimal.ZERO, "");
}
public Data(String id, int iv, BigDecimal zv, String sv) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.iv = iv;
this.zv = zv;
this.sv = sv;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getIv() {
return iv;
}
public void setIv(int iv) {
this.iv = iv;
}
public BigDecimal getZv() {
return zv;
}
public void setZv(BigDecimal zv) {
this.zv = zv;
}
public String getSv() {
return sv;
}
public void setSv(String sv) {
this.sv = sv;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{iv: %d, zv: %s, sv: %s}", iv, zv, sv);
}
}
Data class for VBISAM:
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import dk.vajhoej.isam.KeyField;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Alignment;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Endian;
import dk.vajhoej.record.FieldType;
import dk.vajhoej.record.Struct;
import dk.vajhoej.record.StructField;
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
@KeyField(n=0)
@StructField(n=0, type=FieldType.FIXSTRNULTERM, length=8)
private String id;
@StructField(n=1, type=FieldType.INT4)
private int iv;
@StructField(n=2, type=FieldType.PACKEDBCD, length=4, decimals=2)
private BigDecimal zv;
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public Data2() {
this("", 0, BigDecimal.ZERO, "");
}
public Data2(String id, int iv, BigDecimal zv, String sv) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.iv = iv;
this.zv = zv;
this.sv = sv;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getIv() {
return iv;
}
public void setIv(int iv) {
this.iv = iv;
}
public BigDecimal getZv() {
return zv;
}
public void setZv(BigDecimal zv) {
this.zv = zv;
}
public String getSv() {
return sv;
}
public void setSv(String sv) {
this.sv = sv;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{iv: %d, zv: %s, sv: %s}", iv, zv, sv);
}
}
Utility class:
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class AutoMap<TFROM,TTO> {
public static class MethodPair {
private Method getter;
private Method setter;
private boolean trim;
public MethodPair(Method getter, Method setter, boolean trim) {
this.getter = getter;
this.setter = setter;
this.trim = trim;
}
public Method getGetter() {
return getter;
}
public Method getSetter() {
return setter;
}
public boolean getTrim() {
return trim;
}
}
private List<MethodPair> conv;
public AutoMap(Class<TFROM> from, Class<TTO> to) throws IntrospectionException {
this(from, to, false);
}
public AutoMap(Class<TFROM> from, Class<TTO> to, boolean trim) throws IntrospectionException {
conv = new ArrayList<MethodPair>();
for(PropertyDescriptor pdfrom : Introspector.getBeanInfo(from).getPropertyDescriptors()) {
for(PropertyDescriptor pdto : Introspector.getBeanInfo(to).getPropertyDescriptors()) {
if(pdfrom.getName().equals(pdto.getName())) {
Method getter = pdfrom.getReadMethod();
Method setter = pdto.getWriteMethod();
if(getter != null && setter != null) {
conv.add(new MethodPair(getter, setter, trim && pdfrom.getPropertyType().equals(String.class)));
}
}
}
}
}
public void convert(TFROM from, TTO to) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
for(MethodPair mp : conv) {
if(mp.getTrim()) {
mp.getSetter().invoke(to, ((String)mp.getGetter().invoke(from)).trim());
} else {
mp.getSetter().invoke(to, mp.getGetter().invoke(from));
}
}
}
}
This code may appear excessive compared to the simple D.COB above and the two data classes are actually identical, but the code does provide a lot of extra flexibility.
Changing:
@Struct(endianess=Endian.LITTLE, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
to:
@Struct(endianess=Endian.BIG, alignment=Alignment.ALIGN1)
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
will change integers in the VBISAM files from little endian to big endian (GnuCOBOL default!).
Changing:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50)
private String sv;
to:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50, encoding="ISO-8859-1")
private String sv;
public class Data2 implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=3, type=FieldType.VARFIXSTR, length=50, encoding="utf-8")
private String sv;
will convert the sv field from ISO-8859-1 to UTF-8. Remember if you do that then the field may grow in length!
And:
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=4, type=FieldType.VAXFP4)
private float xv1;
@StructField(n=5, type=FieldType.VAXFP8)
private double xv2;
public class Data implements Serializable {
...
@StructField(n=4, type=FieldType.FP4)
private float xv1;
@StructField(n=5, type=FieldType.FP8)
private double xv2;
will convert xv1 and xv2 from VAX F-float and VAX G-float to standard IEEE 32 bit float (S-float in VMS terminology) and standard IEEE 64 bit float (T-float in VMS terminology).
And AutoMap is just a utility class that does not change for different data classes.
Export.
Code:
from dk.vajhoej.isam import Key0
from dk.vajhoej.isam.local import LocalIsamSource
import Data
import Data2
import AutoMap
isq = LocalIsamSource('test.isq', 'dk.vajhoej.vms.rms.IndexSequential', False)
vbisam = LocalIsamSource('test', 'dk.vajhoej.vbisam.VBISAM', False)
m = AutoMap(Data, Data2)
it = isq.readGE(Data, Key0(' '))
while it.read():
d = it.current()
d2 = Data2()
m.convert(d, d2)
vbisam.create(d2)
vbisam.close()
isq.close()
Run:
$ vbisam_init := $vbidir:vbisam_init.exe
$ javac -classpath /isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/record.jar Data.java Data2.java AutoMap.java
$ define/nolog jython_libs "/vbidir/isam-vbisam.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/isam-vms.jar:/isamdir/record.jar"
$ vbisam_init test 68 0 8
$ jython exp.py
(the vbisam_init is necessary because the ISAM library cannot create an index-sequential file only use an existing one)
Import:
from dk.vajhoej.isam import Key0
from dk.vajhoej.isam.local import LocalIsamSource
import Data
import Data2
import AutoMap
vbisam = LocalIsamSource('test', 'dk.vajhoej.vbisam.VBISAM', False)
isq = LocalIsamSource('test.isq', 'dk.vajhoej.vms.rms.IndexSequential', False)
m = AutoMap(Data2, Data)
it = vbisam.readGE(Data2, Key0(' '))
while it.read():
d2 = it.current()
d = Data()
m.convert(d2, d)
isq.create(d)
isq.close()
vbisam.close()
Run:
$ javac -classpath /isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/record.jar Data.java Data2.java AutoMap.java
$ define/nolog jython_libs "/vbidir/isam-vbisam.jar:/isamdir/isam.jar:/isamdir/isam-vms.jar:/isamdir/record.jar"
$ create/fdl=sys$input test.isq
FILE
ORGANIZATION indexed
RECORD
FORMAT fixed
SIZE 68
KEY 0
SEG0_LENGTH 8
SEG0_POSITION 0
TYPE string
$
$ jython imp.py
(the CREATE/FDL is necessary because the ISAM library cannot create an index-sequential file only use an existing one)
Code (portable):
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. LIST.
ENVIRONMENT DIVISION.
INPUT-OUTPUT SECTION.
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT OPTIONAL D-FILE ASSIGN TO "TEST.ISQ" ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED ACCESS MODE IS DYNAMIC RECORD KEY IS D-ID.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
COPY "D.COB".
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 EOF-FLAG PIC X.
01 IV PIC 9(4) DISPLAY.
01 ZV PIC 9(4)V9(2) DISPLAY.
01 SLEN PIC 9(2) DISPLAY.
01 SV PIC X(50).
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PARAGRAPH.
OPEN I-O D-FILE
MOVE 'N' TO EOF-FLAG
PERFORM UNTIL EOF-FLAG = 'Y'
READ D-FILE NEXT
AT END MOVE 'Y' TO EOF-FLAG
NOT AT END PERFORM PRINT-PARAGRAPH
END-READ
END-PERFORM
CLOSE D-FILE
STOP RUN.
PRINT-PARAGRAPH.
MOVE D-IV TO IV
MOVE D-ZV TO ZV
MOVE D-SLEN TO SLEN
MOVE D-SV TO SV
DISPLAY "(" IV "," ZV "," SV(1:SLEN) ")".
Build and run on VMS:
$ cobol list
$ link list
$ run list
Build and run on Windows:
cobc -Wall -free -conf=le.conf -x list.cob
list
(for VBISAM on VMS drop the .ISQ extension as VBISAM creates .DAT and .IDX files)
| Version | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | February 12th 2023 | Initial version |
| 1.1 | March 4th 2023 | Add VBISAM |
eve See list of all articles here
Please send comments to Arne Vajhøj